
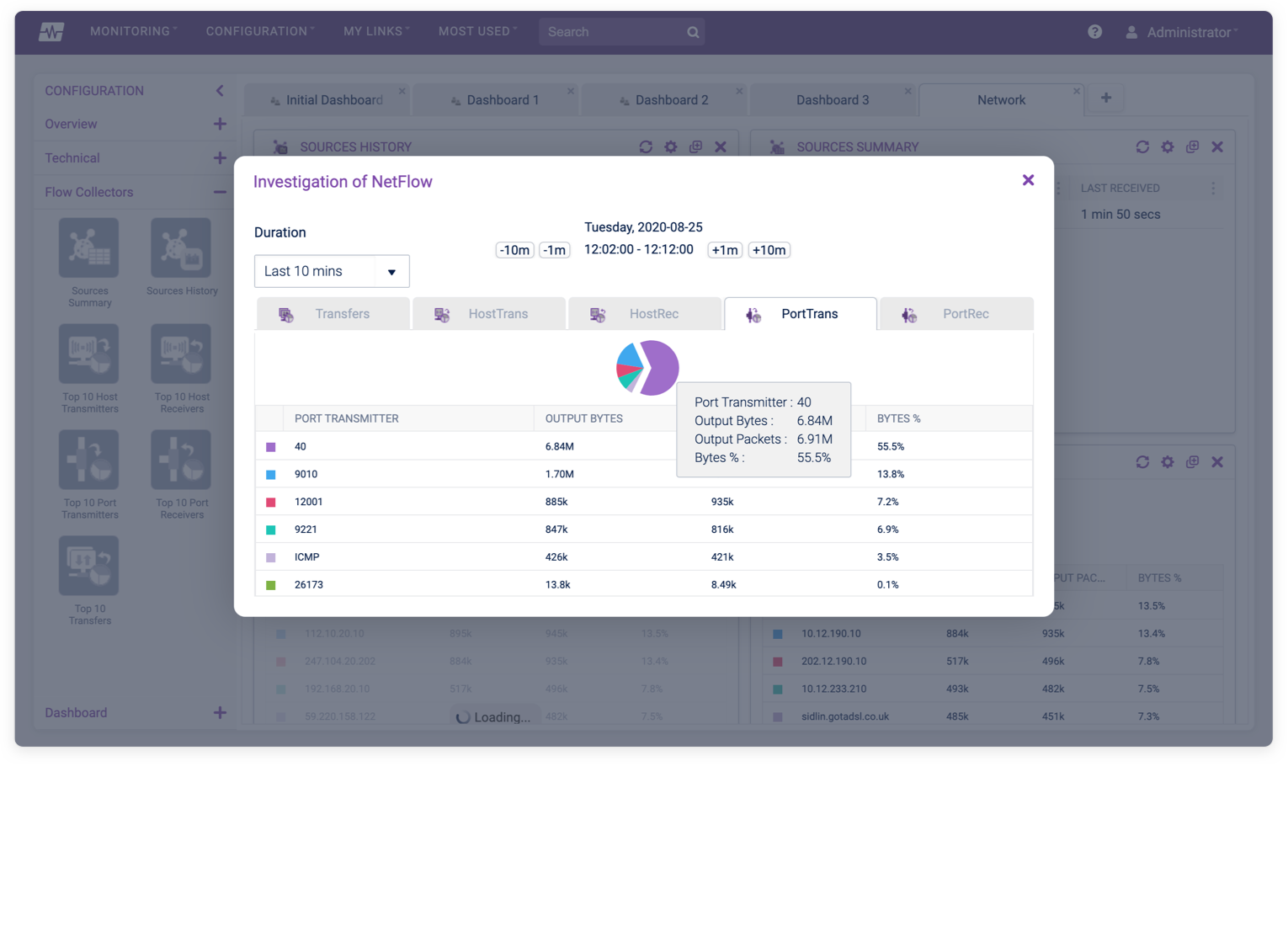
To prevent gaps and spikes in your data, set the cache timeout values. Next, associate the flow record and exporter to the flow monitor we created earlier.Įnter the command record NTArecord followed by exporter NTAexport. We will call it NTAMonitor.Įnter the command flow monitor NTAMonitor. Option application-attributes timeout 300Ĭreating a flow monitor or NetFlow cache is pretty easy. If your device supports Cisco NBAR2 or Next Generation NBAR, and you added collect application name in the flow record, add the following commands to the flow exporter: You can avoid this problem by adding the command template data timeout 60 to set the template to export every minute. To process the data, the template needs to be available to prevent any gaps in data if the server reboots or the NetFlow service is restarted.
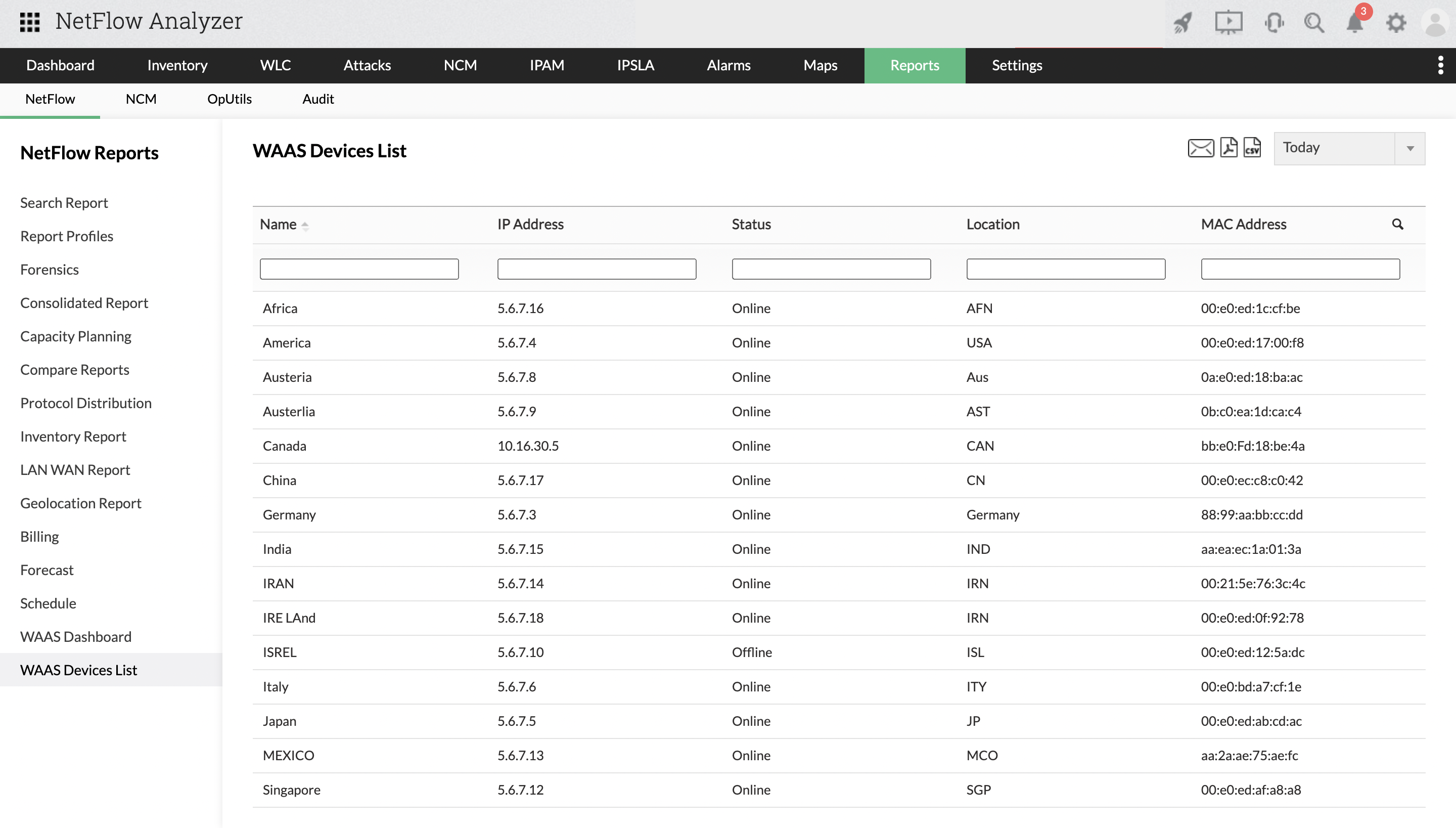
By default, the template is exported every 30 minutes. Next, add the flow protocol type and/or version: export-protocol netflow-v9.įor Flexible NetFlow or NetFlow v9, the template and flow data are exported in two separate packets.
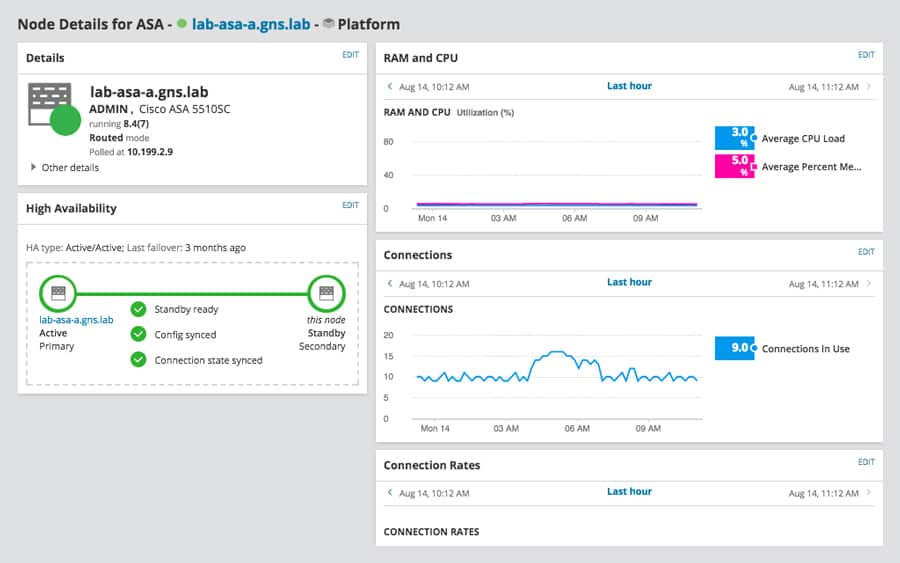
We will type transport UDP 2055 because that's the default port used by SolarWinds NetFlow Traffic Analyzer to listen for network packets. Make sure your interface has a path to your NTA server. The command is source gigabitEthernet 0/1. Next, you'll need to identify the interface that's used to export NetFlow packets from the router. So for this example, type destination 10.199.15.103. The IP address specifies your SolarWinds NetFlow Traffic Analyzer server. Again, you can name the exporter whatever you want. The flow exporter stores information for export, such as the IP address of your flow analyzer tool in SolarWinds ® NetFlow Traffic Analyzer, the UDP port for export, and so on.Įnter the command, flow exporter NTAExport. The next step is to create the flow exporter. If you're using Border Gateway Protocol (or BGP) in your environment, add the following commands to collect AS information: collect routing source as and collect routing destination as. If your device supports Cisco NBAR2 or Next Generation NBAR, add the collect application name command to the flow record. To collect the egress interface data, type collect interface output.Ĭomplete your flow record configuration by entering the following commands: To collect the ingress interface data, enter match interface input. To collect type of service data, type match ipv4 tos. To collect protocol information, enter match ipv4 protocol.įor application port data, type match transport source-port and match transport destination-port. To collect both endpoints of the conversation, enter match ipv4 source address and then match ipv4 destination address.

Next, you'll define match and collect statements to capture fields to include in the flow record. For the purposes of this demo, we'll name it "NTA record," but you can use any name you like. However, in general, there are four basic steps to capturing flow data using Flexible NetFlow: create a flow record, create a flow exporter, create a flow monitor, and apply the flow monitor to interfaces.Īfter you've logged into the router, go into global configuration mode by typing config t. Depending on the Cisco device you are using, there may be additional steps required to successfully collect ingress and egress flow data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
